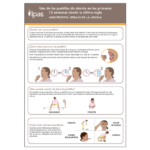
Este material de dos páginas proporciona instrucciones sencillas para utilizar los medicamentos para el aborto de manera segura y tiene como objetivo servir como recurso que los profesionales de la salud pueden compartir con sus pacientes. Está disponible en inglés, español, francés y portugués.
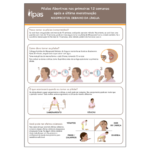
Este material de duas páginas fornece instruções simples para utilizar os medicamentos para o aborto com segurança e tem o objetivo de servir como recurso que os profissionais de saúde podem compartilhar con suas pacientes. Está disponível em inglês, espanhol, francês e português.
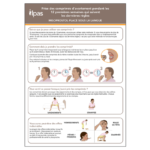
Ce matériel de deux pages fournit des instructions simples pour utiliser les médicaments pour l’avortement sûrement ; il a pour but de servir comme ressource que les prestataires de santé peuvent partager avec leurs patients. C’est disponible en anglais, espagnol, français et portugais.

Este material de dos páginas proporciona instrucciones sencillas para utilizar los medicamentos para el aborto de manera segura y tiene como objetivo servir como recurso que los profesionales de la salud pueden compartir con sus pacientes. Está disponible en inglés, español, francés y portugués.

Este material de duas páginas fornece instruções simples para utilizar os medicamentos para o aborto com segurança e tem o objetivo de servir como recurso que os profissionais de saúde podem compartilhar con suas pacientes. Está disponível em inglês, espanhol, francês e português.

Ce matériel de deux pages fournit des instructions simples pour utiliser les médicaments pour l’avortement sûrement ; il a pour but de servir comme ressource que les prestataires de santé peuvent partager avec leurs patients. C’est disponible en anglais, espagnol, français et portugais.

Este material de duas páginas fornece instruções simples para utilizar os medicamentos para o aborto com segurança e tem o objetivo de servir como recurso que os profissionais de saúde podem compartilhar con suas pacientes. Está disponível em inglês, espanhol, francês e português.

Este material de dos páginas proporciona instrucciones sencillas para utilizar los medicamentos para el aborto de manera segura y tiene como objetivo servir como recurso que los profesionales de la salud pueden compartir con sus pacientes. Está disponible en inglés, español, francés y portugués.

Ce matériel de deux pages fournit des instructions simples pour utiliser les médicaments pour l’avortement sûrement ; il a pour but de servir comme ressource que les prestataires de santé peuvent partager avec leurs patients. C’est disponible en anglais, espagnol, français et portugais.

Este material de duas páginas fornece instruções simples para utilizar os medicamentos para o aborto com segurança e tem o objetivo de servir como recurso que os profissionais de saúde podem compartilhar con suas pacientes. Está disponível em inglês, espanhol, francês e português.
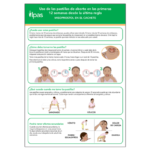
Este material de dos páginas proporciona instrucciones sencillas para utilizar los medicamentos para el aborto de manera segura y tiene como objetivo servir como recurso que los profesionales de la salud pueden compartir con sus pacientes. Está disponible en inglés, español, francés y portugués.
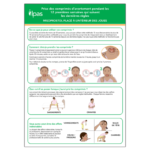
Ce matériel de deux pages fournit des instructions simples pour utiliser les médicaments pour l’avortement sûrement ; il a pour but de servir comme ressource que les prestataires de santé peuvent partager avec leurs patients. C’est disponible en anglais, espagnol, français et portugais.



